In musculoskeletal healthcare, chiropractic and osteopathy are two of the most well-known and widely practised forms of manual therapy. Both are dedicated to improving health by focusing on the musculoskeletal system, particularly the spine, joints, and muscles. However, despite their similarities, chiropractic and osteopathy have distinct principles, techniques, and approaches to patient care. This blog will explore these two professions in detail, comparing their histories, treatment methods, education, and the conditions they commonly treat. Here, you will learn the differences between chiropractic vs osteopathy.
Jump To:
- TLDR – Quick Guide
- 1. Historical Background and Philosophies of Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
- 2. Differences in Techniques and Treatment Approaches of Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
- 3. Education and Training Requirements of Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
- 4. Common Conditions Treated by Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
- 5. Is Chiropractic or Osteopathy Right for You?
- 6. What do I practice at Upright Posture?
- Conclusion – Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs
TLDR – Quick Guide
- Chiropractic and osteopathy both focus on musculoskeletal health but have different approaches.
- Chiropractors emphasize spinal adjustments and nervous system function.
- Osteopaths take a more holistic approach, treating muscles, joints, and circulation.
- Chiropractic is ideal for back pain, neck pain, and nerve-related issues.
- Osteopathy is better suited for broader body dysfunctions, including posture, mobility, and circulation problems.
- The best choice depends on your specific pain points and treatment preferences.
1. Historical Background and Philosophies of Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
While chiropractic and osteopathy have roots in the late 19th century, they were developed independently and based on different philosophies.
Chiropractic was founded by Daniel David Palmer in 1895 in the United States. Palmer’s philosophy centred around the idea that the body has an innate ability to heal itself, but this process can be hindered by misalignments of the spine, which he called “subluxations.” He believed that by correcting these misalignments through spinal adjustments, the nervous system could function properly, allowing the body to heal naturally. This spinal focus remains at the core of chiropractic practice today, with an emphasis on how spinal health impacts overall well-being.
Osteopathy, on the other hand, was developed by Andrew Taylor Still in 1874, also in the United States. Still’s philosophy was more holistic, viewing the body as an interconnected system where structure and function are closely related. Osteopathy emphasises the importance of the body’s ability to self-regulate and heal, but unlike chiropractic, it does not place as much emphasis on the spine alone. Instead, osteopathy takes into account the entire musculoskeletal system, including the bones, muscles, and soft tissues, as well as how they interact with other systems like the circulatory, lymphatic, and nervous systems.
While both professions share the belief in the body’s ability to heal itself, the focus of chiropractic remains more spinal-centred, whereas osteopathy tends to take a more holistic approach, considering the entire body in the context of health and wellness.
2. Differences in Techniques and Treatment Approaches of Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
Chiropractors and osteopaths use manual techniques to treat patients, but the methods and focus of their treatments differ significantly.
Chiropractic Techniques:
Chiropractors are best known for spinal manipulation or adjustments, which involve quick, controlled thrusts to specific spinal vertebrae to restore better motion to the spine. These adjustments are designed to correct spinal subluxations, relieve nerve pressure, and improve mobility. Chiropractic adjustments often produce an audible “crack” or “pop,” which is caused by the release of gas from the joint.
Chiropractors may also use other techniques, such as:
– Mobilisation, a gentler form of movement for restricted joints.
– Soft tissue therapies, including trigger point therapy or myofascial release.
– Exercise prescription to support recovery and prevent future issues.
– Postural advice to improve alignment and reduce strain on the body.
Chiropractic treatment is often short-term and symptom-focused, with many patients seeking care for specific musculoskeletal issues like back pain, neck pain, or headaches.
Osteopathic Techniques:
Osteopaths generally use a broader range of techniques, focusing on the entire body rather than just the spine. They utilise:
– Soft tissue techniques, including stretching, massage, and joint mobilisation.
– Articulation, where joints are moved through their range of motion to improve mobility.
– Muscle energy techniques, where the patient’s muscles are used to assist in stretching or realigning tissues.
– Cranial osteopathy, a very gentle, subtle technique focused on the head and sacrum, is often used for stress, tension, and issues like migraines or sinus problems.
Osteopaths aim to improve circulation, relieve tension, and restore balance to the body as a whole. Their treatments tend to be more holistic, addressing multiple body systems and not just targeting the area of pain.
3. Education and Training Requirements of Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
Chiropractors and osteopaths both undergo rigorous training, but their educational paths differ slightly in terms of focus and structure.
Chiropractic Training:
In the UK, chiropractors are required to complete a four- to five-year undergraduate degree in chiropractic at an accredited institution. This degree includes a combination of academic learning, hands-on practical training, and clinical experience. Chiropractors study subjects such as anatomy, physiology, neurology, pathology, and diagnostic imaging, with a strong emphasis on the biomechanics of the spine and musculoskeletal system. As part of their training, students must complete a supervised clinical internship to gain practical experience in diagnosing and treating patients.
Once qualified, chiropractors must register with the General Chiropractic Council (GCC) to practise legally in the UK. Continuous professional development (CPD) is also a requirement to maintain registration.
Osteopathic Training:
Osteopaths in the UK typically complete a four- to five-year undergraduate degree in osteopathy, which also combines academic learning with clinical experience. The course covers areas such as anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and pathology, but osteopathy students also study a wider range of subjects related to holistic healthcare, including nutrition, psychology, and preventative medicine.
After completing their degree, osteopaths must register with the General Osteopathic Council (GOsC) to practise legally. Like chiropractors, osteopaths are required to engage in continuous professional development to stay up-to-date with the latest research and techniques.
Both professions require a deep understanding of anatomy and musculoskeletal health, but the educational focus for chiropractors is more spine-centric, while osteopaths receive a broader education that includes the wider musculoskeletal and bodily systems.
4. Common Conditions Treated by Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
Chiropractors and osteopaths both treat a wide variety of musculoskeletal conditions, but they are often approached differently based on the practitioner’s philosophy and techniques.
Chiropractors are most commonly sought out for issues related to the spine and nervous system, including:
– Back pain (lower, middle, and upper)
– Neck pain
– Headaches and migraines, often stemming from tension in the neck or upper spine
– Sciatica, a condition caused by irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve
– Whiplash or other trauma-related injuries
– Joint pain in the limbs, such as shoulders, elbows, and knees
Chiropractic care is often used to relieve specific symptoms and improve overall spinal health. Many patients seek chiropractic treatment when they experience acute pain or discomfort.
Osteopaths, on the other hand, treat a wider range of conditions, not limited to musculoskeletal complaints. Common issues treated by osteopaths include:
– Muscle and joint pain, including back, neck, and shoulder pain
– Sports injuries, such as sprains, strains, and overuse injuries
– Arthritis and associated stiffness or joint pain
– Digestive issues, which osteopaths believe can be linked to the musculoskeletal system
– Stress and tension-related conditions, including headaches, fatigue, and anxiety
Osteopathy’s broader approach means that osteopaths may treat a wide variety of health issues, both musculoskeletal and systemic, working to restore balance and function to the entire body.
5. Is Chiropractic or Osteopathy Right for You?
When deciding between chiropractic vs osteopathy, the right choice often depends on your specific needs, preferences, and the nature of your condition. While chiropractic and osteopathy share similarities in their manual therapies and the goal of improving musculoskeletal health, they differ significantly in philosophy, techniques, and treatment scope. Chiropractic tends to focus on spinal health and the nervous system, while osteopathy adopts a more holistic view of the body’s interconnected systems. However, many practitioners undergo further training after graduation which can give them a wide scope of knowledge, skills, and practice. This can mean that the methods and techniques any given practitioner uses can have quite a lot of overlap between the two professions.
6. What do I practice at Upright Posture?
I have my foundational education in Chiropractic but I quickly realised its limitations and spent several years studying advanced topics and techniques including specialised paediatric care for babies and children. I found that the manual techniques that both chiropractors and osteopaths use often were misaligning spines rather than realigning them. After almost leaving the profession due to this shocking finding I was led to a method called Advanced BioStructural Correction (ABC) and after 10 years of using and mastering this method I believe is the most holistic musculoskeletal realignment method available.
Advanced BioStructural Correction is a chiropractic technique developed by Dr. Jesse Jutkowitz. It focuses on addressing postural and structural imbalances in the body, specifically, those caused by misalignments of the spine and other skeletal structures throughout your body. The key concept behind ABC is that the body cannot self-correct certain misalignments (particularly those in the spine), which over time can lead to compensatory patterns, pain, and dysfunction.
Here’s a little more about the method:
Key Principles of ABC:
- Unwinding Structural Imbalances: ABC practitioners aim to correct “primary” misalignments—those the body cannot naturally self-correct. These primary misalignments cause the body to adapt or compensate, leading to secondary imbalances.
- Posture and Spinal Alignment: The technique places significant emphasis on improving posture. Practitioners use specific adjustments to realign the spine and other body structures, helping the body “unwind” from years of compensations.
- Soft Tissue and Muscle Tension: ABC doesn’t focus on muscle tension directly as a cause of pain but sees it as a result of misaligned structures. The theory is that once the skeletal structure is corrected, the soft tissues will naturally relax and pain will subside.
- Breathing and Mobility: One of the notable aspects of ABC is the impact it can have on breathing and body movement. By restoring proper alignment, patients become effortlessly upright, breathe easier, and have improved mobility.
- Organ function: As your body posture is improved, organ stretch, twist and compression are reduced. Often patients report feeling more awake and alert, have better circulation and digestion, better mood and improved sleep. Together, these changes can completely transform someone’s health.
ABC Treatment Process:
ABC treatments uniquely involve stretches to the spine to release scar tissue called meningeal adhesions followed by manual corrections to misalignments focusing primarily on the vertebrae, ribs, pelvis, feet and skull. The corrections are designed to correct these primary misalignments in a specific order, based on the body’s compensatory patterns. Patients often experience an immediate postural shift after treatment, which can result in noticeable relief or changes in how they stand or move.
This method can be used to provide symptom relief but also with continued care helps to return your body to a much better overall condition in a process called UNWINDING.
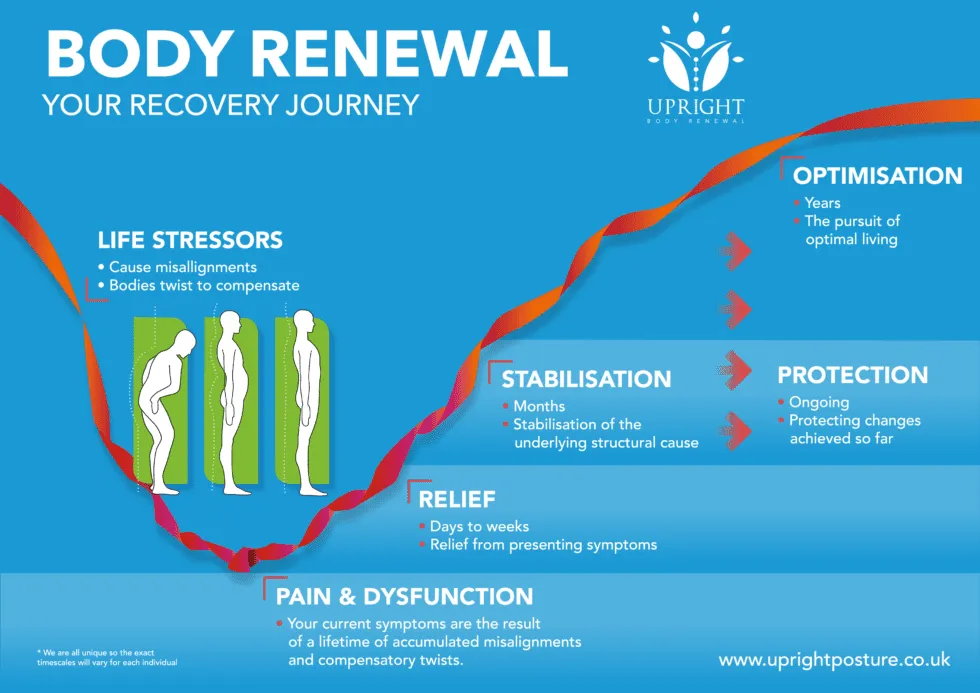
Conclusion – Chiropractic vs Osteopathy
Both professions require extensive education and training, and both have their strengths in treating a variety of conditions. By understanding the differences between chiropractic and osteopathy, you can make a more informed choice about which approach might best suit your healthcare needs.
It is also good practice to contact several different chiropractic and osteopathic clinics to find out if their expertise and services fit your particular needs. There is plenty of choice in most parts of the UK.
You can find a full list of registered practitioners and clinics below.
Of course, we would be delighted if you get in touch with us to see if we can help you reattain levels of health and ability that you may not have experienced for years (or even decades)!
By Lucky Gidda – Chiropractor and ABC Practitioner
Key Takeaways
- Chiropractors specialize in spinal adjustments to improve nervous system function.
- Osteopaths focus on whole-body health, using soft tissue techniques and joint mobilization.
- Chiropractic is often sought for acute pain relief and nerve-related issues.
- Osteopathy can address a wider range of conditions, including circulatory and digestive concerns.
- Both professions require medical training, but their methodologies and treatment styles differ.
- Choosing between them depends on your symptoms, health goals, and treatment preference.
FAQs
Which is better for back pain, chiropractic or osteopathy?
Chiropractic is often more effective for back pain caused by spinal misalignment, while osteopathy may be better for overall posture and mobility issues.
Do chiropractors and osteopaths require medical training?
Yes, both undergo extensive medical training, but osteopaths typically receive broader education in general medicine.
Can osteopathy or chiropractic help with headaches?
Yes! Chiropractic adjustments can relieve tension headaches and migraines, while osteopathy may help by improving circulation and muscle tension.
Are chiropractic adjustments safe?
Yes, when performed by a qualified professional, chiropractic adjustments are safe, though mild soreness can occur post-treatment.
How do I decide which one to visit?
If you have nerve-related pain or spinal issues, try chiropractic. If you need a more holistic, full-body approach, osteopathy might be better.